Imagine a website that loads almost instantly—interactive before you even realize it. How would that transform your browsing experience?
In today’s digital landscape, fast-loading websites aren’t just a luxury—they’re essential. Since 2010, Google has factored site speed into its search rankings, making performance a key component of online visibility.
So, what qualifies as “fast”? While there’s no absolute benchmark, a page load time of under two seconds is generally considered optimal. Today’s users expect near-instant access to information. If your website takes longer than a few seconds to load, you could be losing potential customers not to mention slipping in search engine rankings.
Here’s a powerful insight: according to the Aberdeen Group, even a one-second delay in page loading can result in a 7% drop in conversions, 11% fewer page views, and a 16% decline in customer satisfaction. These figures underscore just how critical speed is to your digital success.
What is Site Speed?
Site speed—often referred to as page speed—measures how quickly the content on a page loads and is displayed on a user’s device. Simply put, it reflects how fast someone can begin interacting with your website after clicking a link or entering your URL. This metric is crucial, as it directly impacts user experience (UX), engagement, and search engine rankings.
But how exactly does Google evaluate site speed? Do they focus on the time it takes for the entire page to load?
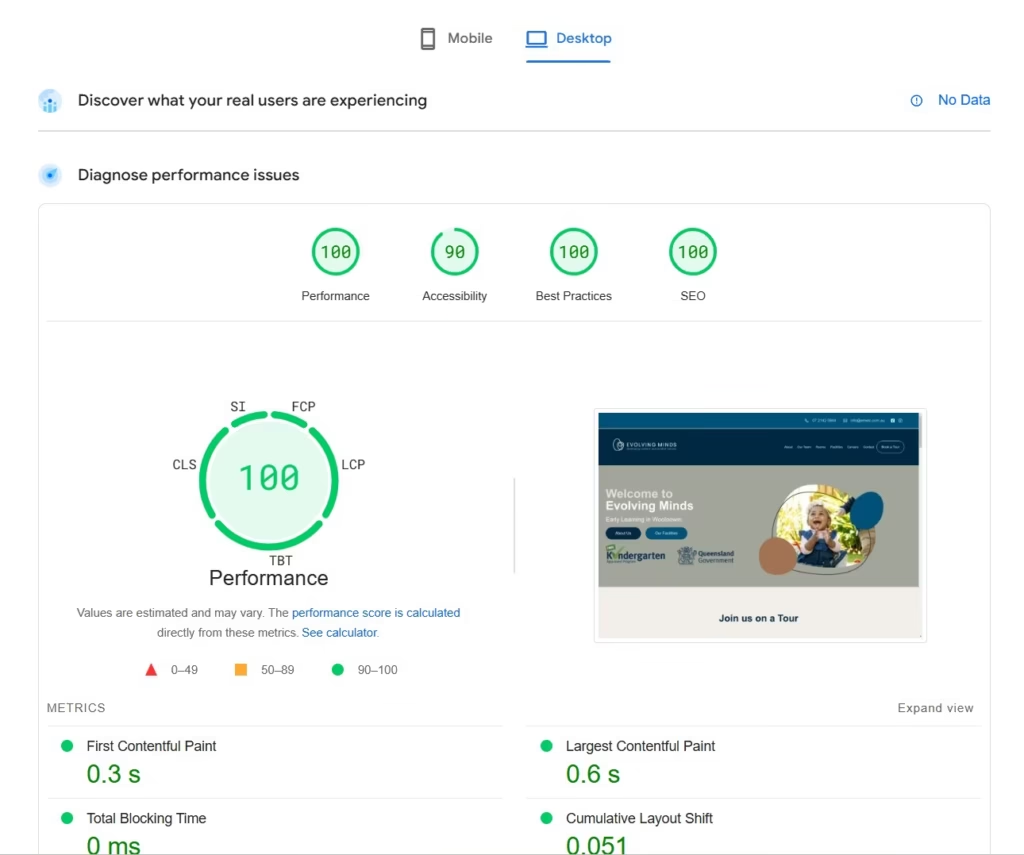
While Google hasn’t explicitly confirmed a single evaluation method, the detailed data provided in their PageSpeed Insights tool indicates that they likely assess multiple speed-related metrics.
Key Page Speed Metrics
To accurately evaluate and improve your website’s speed, it’s important to understand the key performance indicators—especially Google’s Core Web Vitals, which are designed to measure user experience on web pages:
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): Measures the time from when the page begins loading to when any content is first rendered on screen.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Replacing First Input Delay (FID), INP provides a more complete measure of responsiveness. Aim for an INP below 200 milliseconds to maintain smooth user interactions.
- Total Blocking Time (TBT): Indicates the total time the page is blocked from responding to user input, usually due to long script execution.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Assesses loading performance. A good target is for LCP to occur within 2.5 seconds of the page starting to load.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Evaluates visual stability by measuring unexpected layout shifts. A score under 0.1 is considered optimal for a seamless experience.
- Speed Index (SI): Reflects how quickly the visible parts of a page are populated, helping to gauge perceived load speed.
Other Important Metrics
- Time to First Byte (TTFB): Measures how long it takes for the browser to receive the first byte of data from your server. It’s a key diagnostic for backend performance.
- Time to Interactive (TTI): Indicates when the page becomes fully interactive and responsive to user actions.
Why is Website Speed Important?
Website speed goes beyond technical performance, it has a direct impact on user perception, emotional response, and business results. Every second matters, not just for SEO rankings, but for genuine user engagement and your overall bottom line.
User Experience (UX): The Emotional Impact of Site Speed
Slow-loading websites are more than just a technical flaw—they’re a major source of user frustration and lost engagement.
Picture a user trying to make a quick purchase or access important information, only to be stalled by a sluggish loading bar. These moments of friction directly lead to higher bounce rates and reduced user satisfaction.
According to the latest statistics from Neil Patel, 47% of users expect a webpage to load in under two seconds, and a delay of just two seconds can increase bounce rates by up to 103%.
Search Engine Optimisation (SEO): Speed Influences Visibility
Google has long identified website speed as a key ranking factor. Fast-loading sites tend to offer a better user experience, which aligns with Google’s goal of delivering relevant and efficient results.
With the introduction of Core Web Vitals, metrics such as Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) have become vital indicators of performance and user experience.
Slow site speed doesn’t just test user patience—it can negatively impact your search rankings, reducing visibility and potential organic traffic.
Speed Drives Conversions for Businesses Across the Globe
The connection between website speed and business performance is both measurable and significant. Faster websites consistently see better conversion rates and higher revenue.
Take Amazon, for example: they estimated that a one-second delay in page load could cost them $1.6 billion in annual sales. Google reported that a slowdown of just 0.4 seconds in search results could lead to 8 million fewer searches per day, drastically reducing ad impressions.
In the eCommerce industry, up to 40% of users will abandon a website entirely if it takes longer than three seconds to load.
These statistics clearly demonstrate that boosting your website speed doesn’t just enhance UX—it has a direct, tangible impact on your bottom line by turning user frustration into user action.
How to Check Your Page Load Time?
Before making any optimisations, it’s essential to assess your website’s loading speed. Tools such as Google PageSpeed Insights and GTMetrix offer a clear benchmark of your site’s performance and highlight specific areas that need improvement.
This initial step is crucial—because effectively optimising page load time begins with understanding your current performance.
7 Ways to Improve Your Site Speed for Better SEO Results
Improving your website’s speed is essential not only for delivering a smooth user experience but also for boosting your SEO performance. Let’s explore how to enhance your website speed through effective page speed optimisation techniques.
After analysing your site speed, use the results to identify the specific elements that are slowing down your site. Optimising your website is not about applying random fixes—it’s about strategically addressing the factors that have the greatest impact on performance.
Here are seven proven methods to help you speed up your website:
1. Image Optimisation: Essential for Loading Speed
Optimise Image Formats
Selecting the correct image format plays a key role in balancing visual quality with fast load times. For example:
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): Best suited for photographs due to its efficient compression of high-quality images into smaller file sizes. As a general rule: if the image contains many colours, gradients, or textures, JPEG is ideal.
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics): More suitable for images with fewer than 16 colours or when transparency is needed. However, PNGs tend to have larger file sizes, which may affect loading speed.
- WebP (Web Picture Format): Offers advanced compression, making it suitable for both photos and graphics. WebP can reduce file sizes by up to 25% compared to JPEG and PNG, while maintaining higher image quality.
Compress Images
Image compression reduces file size without sacrificing noticeable quality, helping your pages load faster.
According to Pingdom, images contribute to approximately 53% of a web page’s total weight, meaning they play a major role in how quickly your site loads—and, by extension, your overall performance.
Tools such as TinyPNG can automate the image compression process, helping to reduce load times and minimise bandwidth usage—ultimately enhancing your website’s overall speed. For WordPress users, plugins like ShortPixel are excellent for optimising images across your entire media library efficiently.
2. Enable Browser Caching
Enabling browser caching allows web page data to be temporarily stored in a user’s browser, resulting in significantly faster load times for returning visitors.
To configure browser caching based on your server type:
- For Apache servers: Edit the .htaccess file to set both the Expires and Cache-Control headers to a future date. If you’re using WordPress, consider plugins like W3 Total Cache or FastPixel, which are compatible with Apache servers.
- For Nginx servers: Modify the nginx.conf file to include appropriate caching directives. The most effective method for setting up caching on Nginx is through FASTCGI caching. For WordPress users, WP Rocket is recommended—it’s user-friendly and provides excellent customer support, reducing the need for manual configuration.
- For LiteSpeed servers: Take advantage of the built-in caching capabilities, or use the LiteSpeed Cache plugin, especially for WordPress and other content management systems.
3. Minify JavaScript, CSS, and HTML
Minification is the process of removing unnecessary characters—such as spaces, line breaks, and comments—from your source code without altering its functionality. In simpler terms, it’s about compressing your code for better performance.
By minifying your JavaScript, CSS, and HTML files, you significantly reduce their file size, which decreases the amount of data that needs to be transferred—resulting in faster page load times.
Below is a side-by-side comparison:
- The left side shows the original code with extra spaces and comments.
- The right side displays the minified version, where all non-essential elements have been removed to optimise and compress the code.
Original Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=”en”>
<head>
<meta charset=”UTF-8″>
<title>Sample Page</title>
<style>
/* Main container style */
.container {
margin: 20px;
padding: 30px;
border: 1px solid #ccc; /* Light grey border */
font-family: ‘OpenSans’, sans-serif;
}
/* Header style */
.header {
font-size: 24px;
color: navy;
}
</style>
<link href=”path/to/full/OpenSans-Regular.ttf” rel=”stylesheet”>
</head>
<body>
<div class=”container”>
<h1 class=”header”>Welcome to My Page</h1>
<p id=”demo”>This is a demonstration paragraph.</p>
</div>
<script>
// Function to change the text of the paragraph
function changeText() {
document.getElementById(“demo”).innerHTML = “Text updated!”;
}
// Change text on page load
window.onload = function() {
changeText();
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
Minified Code
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang=”en”><head><meta charset=”UTF-8″><title>Sample Page</title><style>.container{margin:20px;padding:30px;border:1px solid #ccc;font-family:’OpenSans’,sans-serif}.header{font-size:24px;color:navy}</style><link href=”path/to/minified/OpenSans-Regular.woff2″ rel=”stylesheet”></head><body><div class=”container”><h1 class=”header”>Welcome to My Page</h1><p id=”demo”>This is a demonstration paragraph.</p></div><script>function changeText(){document.getElementById(“demo”).innerHTML=”Text updated!”}window.onload=function(){changeText()};</script><
4. Reduce Redirects
Each redirect triggers an additional HTTP request, which can significantly slow down your website’s load time. For example, when a URL goes through multiple redirects (known as a redirect chain), the server must process each step—delaying the final page load.
By eliminating unnecessary redirects, you streamline the path data takes, resulting in faster load times and improved overall site speed.
5. Use a CDN (Content Delivery Network)
For websites with a global audience, implementing a Content Delivery Network (CDN) is crucial for ensuring fast and reliable access from anywhere in the world. Learn More abour CDNs and how they improve speed.
A CDN works by storing cached versions of your website across multiple geographic locations, known as Points of Presence (POPs). When a user visits your site, content is served from the POP closest to their physical location, significantly reducing latency and load times.
Leading websites use CDNs to deliver content quickly to users worldwide. For example, a media platform might rely on a CDN to efficiently stream videos to international viewers, drastically improving load speeds and overall user experience.
6. Mobile-First Indexing: Prioritising Speed on the Smallest Screens
With Google’s mobile-first indexing, the performance of your mobile site is more critical than ever. Mobile users demand fast, seamless access to content and services—regardless of where they are or what device they’re using.
A one-second improvement in mobile site speed can increase conversion rates by up to 27%.
A slow mobile experience risks alienating this ever-growing user base, which can hurt both your SEO rankings and potential revenue.
However, mobile optimisation involves more than just speed—it’s about delivering an experience tailored to the unique nature of mobile devices. Key factors include:
- Responsive Design: Ensures your website adjusts smoothly to various screen sizes and resolutions.
- Touch Optimisation: Enhances usability by making the interface easy to navigate and interact with on touchscreens.
- Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP): A framework that delivers lightweight, stripped-down versions of web pages for lightning-fast load times on mobile.
- Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): Websites that function like native apps, offering features such as offline access, push notifications, and improved engagement.
By prioritising mobile optimisation, you ensure your website delivers a fast, seamless, and engaging experience for every visitor—no matter what device they’re using.
7. Choose a Better Hosting Service
Your website’s hosting environment has a significant impact on its overall speed. Think of it this way: even the most perfectly optimised website will still perform poorly if it’s hosted on a slow or overcrowded server.
When selecting a hosting provider, consider the following key factors:
- Server Location: Choose a hosting server that’s geographically close to your target audience. This minimises data travel time and results in faster load speeds.
- Server Resources: Make sure the hosting plan offers sufficient CPU, RAM, I/O capacity, and storage to support your site’s traffic and content demands.
Server Technology: Opt for hosts that use modern infrastructure, such as solid-state drives (SSDs) and performance-optimised server software, to ensure better reliability and faster response times.
Quick Tip: If your hosting plan costs only around $6.99/month, it’s unlikely your site will load quickly. This sluggish performance usually results from sharing server resources with numerous other websites, which can seriously slow down your site’s speed.
Looking for a hosting provider that meets all your needs? Consider DigiTotal. We provide a superior hosting solution tailored to your requirements, focusing on speed, security, and reliability.
Final Thoughts
Recognising the vital importance of website speed reveals its strong influence on user satisfaction, SEO, and overall business success. Slow load times cause frustration, reduce engagement, and ultimately harm your bottom line.
By applying key optimisation techniques—such as compressing images, enabling browser caching, minimising redirects, and using a CDN—you can significantly improve your website’s performance. These simple yet powerful changes can lead to higher user engagement, improved search rankings, and increased conversions, as visitors encounter fewer obstacles in interacting with your content.
Improving your site’s speed is essential in today’s competitive digital landscape. It ensures a smooth, seamless experience that encourages users to stay longer and engage more meaningfully.
Ultimately, boosting your website’s speed is about more than just technical enhancements—it’s about building a more effective, enjoyable online environment for your visitors.

